Research Highlights
Vol.6, February 2016
Surveillance of a novel norovirus variant
Norovirus is a major causative pathogen of viral gastroenteritis in people, leading to vomiting and diarrhea. Until recently, global outbreaks of norovirus have mainly been caused by genotype GII.4. However, a new variant norovirus strain was prevalent in Japan in the winter of 2014–2015. This novel norovirus was a genotype GII.17 variant.
To investigate the genetic mutations that have occurred in the norovirus GII.17 strains, Hideaki Shimizu and co-workers at the Kawasaki City Institute for Public Health, Kanagawa, and collaborating Japanese researchers conducted whole genome sequencing of the new variant including other GII.17 strains circulating in our country from 2013 to 20151.
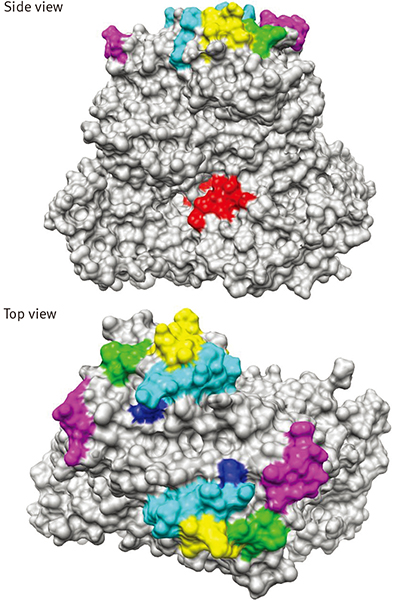
The team used next-generation sequencing techniques to analyse six GII.17 strains that were available in Japan from 2013 to 2015. All strains were assigned to GII.17 in the VP1 gene, which codes a major capsid protein of norovirus. However, the norovirus genotyping server could not characterize RNA polymerase genotypes of the strains, which indicates the norovirus contains novel sequences. Therefore, Shimizu and his team also inferred a potential of genetic mutations within the capsid region of the strains.They named the variant as Hu/GII/JP/2014/GII.P17-GII.17.
They found that the GII.17 strain circulating in Japan in November 2014 to March 2015 was a novel variant with several amino acid substitutions in the RNA polymerase and capsid regions.
Further phylogenetic analysis of norovirus shows the emergent strain has quietly been circulating in Asia from 2013. Also, it appears to undergo an evolutionary history diverse from other previous GII.17 strains.
The researchers call for careful monitoring of the new GII.17 variant, because it may trigger global outbreaks in future due to the potential to evade the host’s immune system.
Reference and affiliations
- Y. Matsushima1,2, M. Ishikawa1, T. Shimizu1, A. Komane1, S. Kasuo3, M. Shinohara4, K. Nagasawa5, H. Kimura5, A. Ryo2, N. Okabe1, K. Haga6, Y.H. Doan6, K. Katayama6, H. Shimizu1.
Genetic analyses of GII.17 norovirus strains in diarrheal disease outbreaks from December 2014 to March 2015 in Japan reveal a novel polymerase sequence and amino acid substitutions in the capsid region. Euro Surveillance 20 (26): pii=21173 (2015) - Division of Virology, Kawasaki City Institute for Public Health, Kanagawa, Japan
- Department of Microbiology, Yokohama City University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan
- Division of Infectious Diseases, Nagano Environmental Conservation Research Institute, Nagano, Japan
- Division of Virology, Saitama Institute of Public Health, Saitama, Japan
- Infectious Disease Surveillance Center, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan
- Department of Virology II, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan
*Correspondence: shimizu-h@city.kawasaki.jp
Figure: